A number line is a visual tool used in mathematics to show the position of numbers in order. It is drawn as a straight horizontal line, and each point on the line represents a number (any type of real number e.g. integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, etc.).
The numbers on the number line are ordered such that they become larger going to the right and smaller going to the left. If we show 0 on the number line, then any number on the left of zero is negative (since any negative number is smaller than 0). Similarly, any number to the right of 0 must be postive.
Example 1: Represent -4, -0.2, 0, 5, 7.8 on a number line
We’ll start by drawing a horizontal line, with an arrow on the right:

Since 0 is one of the numbers to represent on the number line, let’s put in 0 first.
All negative numbers should be to the left of 0, since they are smaller than 0. All positive numbers should be to the right of zero, since they are greater than 0.
Hence, -4, and -0.2 should be to the left of 0; 5 and 7.8 should be to the right of 0.
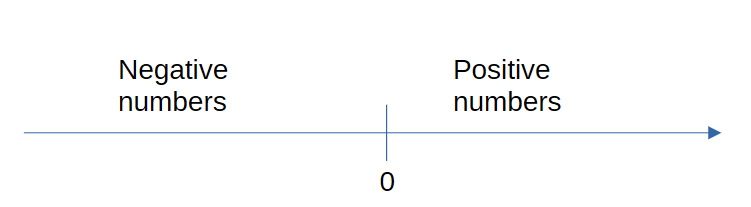
The smaller the number, the more it lies on the left. The larger the number, the more it lies on the right of the number line.
Hence, here’s how -4, -0.2, 0, 5 and 7.8 are on the number line:

Number lines are useful to help us comparing numbers. By learning how to represent numbers correctly on a number line, students can develop stronger number sense, which is important for building confidence in solving more challenging math problems in the future.
